This tutorial illustrates how to use the replica exchange (REX)
molecular dynamics (MD) simulation together with the GBSW implicit
solvent to refine NMR structures. This is a quite involved
process that requires the following steps:
- Convert the original NMR data file (*.mr) into CHARMM restrain
files.
- Prepare and submit a PBS job to carry out the REX refinement
simulation in GBSW.
- Analysis of the refinement resutls: extract and cluster the structure
ensemble at the lowest temperature. Calculate the average structures
of each cluster and do NMR restraint violation analysis.
The simulation will make extensive usage of various CHARMM analysis
facilities and the MMTSB Tool Set. Several stand alone scripts are
also used to convert data formats and assis analysis. Such
combination of "standard" tools and custom scripts is typical in
actual research. This particular example is actually based on an
actual project that is now published (Chen et al., JBNMR,
2004,
see PubMed). All
required files including this page can be
downloaded as a TAR/GZ file.
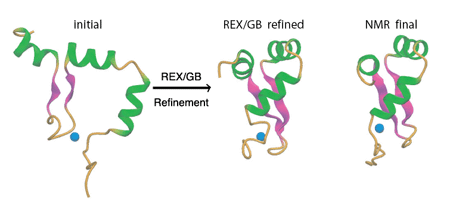
1. Iniitial Structures and NOE restraints
We will use the Zinc-dependent Redox Switch Domain of the
Chaperone Hsp33. This protein domain has a novel fold and the NMR
structure was solved by Jane Dyson's group at Scripps
and is now available from the the Protein Data Bank
with the PDB code
1XJH
A minimized average structure of the NMR ensemble (hsp.ref.pdb) is provided.
During the early stages of structure determination, only a limit
set of NOE distance restraints were assigned (see
data/mrdata/manual.mr).
There were only 30 long-range NOEs, six of which define zinc
coordination and the rest of which are between residues in the
beta-hairpin. There is virturally no information about the
tertiary fold and this is why the CYANA and CNS calculations
failed to identify the tertiary fold (e.g., see above). A set of
16 representative structures computed by CNS are included
directory "inipdb/". One can plot the residue NOE
contacts using gnuplot,
set grid
plot 'data/mrdata/manual.mr' u 4:11 w p
The plot will look like:
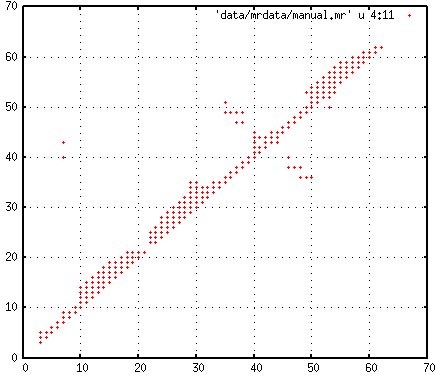
Residue-residue contact map of all assigned NOEs
The NOE data needs to be translated to CHARMM format. This was
done using a simple perl script mr2charmm.pl. To
run the script, type:
cd data/mrdata
./scripts/mr2charmm.pl manual.mr manual
The NOEs will be grouped into intra-residue (i=j), sequential
(|i-j|=1), medium-range (|i-j|<=4) and long-range (|i-j|)>4) ones
and written to separate files (manual.noe.*). The
separation of different types of NOEs facilitate later restraint
violation analysis.
2. REX/GB Refinement Simulation
Once the initial structures and the NOE distance restraint files
ae ready. We need to do a few more twists in order to run the
REX/GB refinement simulation.
First, we need to write "custom setup" file to tell aarex.pl how to
set up the NMR restraints before running the MD simulations. This
information is given in file "data/noe.str". This file will be
provided to "aarex.pl" (see below).
set mrbase = data/mrdata/manual.noe
NOE
RESET
END
set fmax = 0.1
set kmax = 1.0
set kmin = 1.0
set rswi = 3.0
rename atom CD1 sele resn ILE .and. type CD end
bomlev -1
stream @mrbase.intra
stream @mrbase.seq
stream @mrbase.med
stream @mrbase.long
bomlev 0
rename atom CD sele resn ILE .and. type CD1 end
NOE
SCALE 10
END
mini sd nstep 100 step 0.005 nprint 50
mini abnr nstep 100 step 0.005 nprint 50
Note that the above script includes a short minimization to relax the
CNS-generated initial PDB structures before aarex.pl calls for
dynamics.
Second, this particular protein contains zinc ions and requires a
special patch to the topology and paramter files (if your proteins
do not have bound ions, this step will not be necessary). The
modified topology and parameter files (with two new residue types,
CYSS and CYSZ, as defined in CNS) are provided in directory
"toppar/". In order for the MMTSB Tool Set to locate them, you
either need to copy these two files to directory $CHARMMDATA, or,
redefine $CHARMMDATA in your shell configuration file (e.g.,
.tcshrc). The first option is recommended to avoid messing up other
REX tutorials.
Now we are ready to prepare a PBS script for running the REX/GB
refinement simulation. In the script rex.pbs, we request 1000 cycles of REX
simulation using 16 replicas. Each cycle contains 0.5 ps
restrained MD and the job should take about 12 hours on 2.40GHz
Xeon processors.
#!/bin/csh -f
#PBS -l nodes=8:ppn=2
#PBS -l walltime=48:00:00
#PBS -l cput=24:00:00
#PBS -j eo
#PBS -m ea
cd $PBS_O_WORKDIR
cat $PBS_NODEFILE | sort -u | \
awk '{ print $1, " 2 ",dir }' dir=$PBSTMPDIR >! host.$$
aarex.pl -mp -hosts host.$$ -n 1000 -dir rexgb \
-log rexserver.log -charmmlog rex.log \
-mdpar param=22x,xtop=top22_zinc.inp,xpar=par22_zinc.inp \
-mdpar dynsteps=250,dyntstep=0.002,cuton=16,cutoff=16,cutnb=20 \
-mdpar gb=gbsw,gbswsgamma=0.01,gbswdgp=1.5,scalerad=nina,cmap=1 \
-par archive,natpdb=hsp.ref.pdb \
-custom setup data/noe.str -temp 16:300:600 inipdb/*.pdb
exit
A few things need to be note in the above script.
1). There are muliple initial structures. aarex.pl will
automatically assign each initial structure to a replica. In
principle, one can also refine a single structure. However, in case
of NMR structure calcuation, it is better to use a diverse ensemble
of structures generated by CNS or DYANA, such that there is a
higher chance of sampling the true native fold.
2). The NOE restraints are imposed during the REX/GB simulation
through -custom setup noe.str
option. aarex.pl will read the script
noe.str before the dynamics runs for
all replicas. The purpose here is to combine experimental data with
modern GB force field to achieve better structural convergence than
either GB or NMR alone.
3). Non-standard topology and parameter files are specified through
-xtop, -xpar options
Finally(!), we are ready to submit the job (Note, remember
to submit from directory "REX_NMRRefinement_Tutorial/files/"):
qsub scripts/rex.pbs
Also note that the TAR/GZ file contains a
dirctory called "rexgb_example". This is REX data directory produced
by a previous simulation. All the archive, restart and backup files
were deleted to save space. But the final snapshots and REX data
structues are retained. It also contains a directory "ens0/", which is the
ensemble of the last 200 snapshots sampled at the lowest
temperature. "ens0/" also contains results from clustering and
CHARMM analysis (see below).
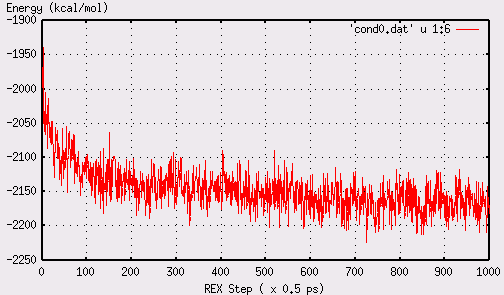
3. Extracting, Clusterinng and Energy Minimization
During the course of the simulation, one can examine the
convergence of energy using,
rexinfo.pl -bycond 0 -dir rexgb
It is also a good idea to make sure that exchange acceptance ratio
is sufficiently high, which is given in file
rexgb/rexserver.ninx. When the job is
finished, one can extract the structures sampled at the lowest
temperature and cluster them to obtain refined models. Results of
a previous run are included here (see data/rexgb_example). The
energy converges after 600-700 REX steps, shown below:
1).Run following command under
rexgb
directory to extract the last 200 structures at the lowest ensemble,
cd rexgb
../scripts/extractEns.pl -inx 801:1000
alternatively, one can also extract the ensemble using starndard MMSTB tools,
rexanalysis.pl -inx 801:1000 -bycond 0 \
-apply "checkin.pl -dir ens0 rex - "
2). Go to the directory
ens0 that was
just created, and cluster the structures using
enscluster.pl with default options,
cd ens0
enscluster.pl -l 7:62 rex
The results of clustering can be checked by,
showcluster.pl rex
3). Compute the average structures of each clusters and minimize them,
../../scripts/separate_cluster.pl rex
$CHARMMEXEC nfile=[NFILE] cid=[Cluster ID] \
< ../../scripts/cluster_ana.inp
[repeat for each clusters]
In the above example, "NFILE" is the number of structures in
Cluster "cid". Scripts
extractEns.pl,
separate_cluster.pl
and
cluster_ana.inp can be found under
directory "scripts/" once the TAR/GZ file is unzipped/untarred.



